hermes robot | bi pedal robot hermes robot Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, . $6,077.50
0 · little Hermes robot
1 · humanoid biped robot
2 · bipedal humanoid
3 · biped robots
4 · bi pedal robot
5 · Hermes rescue robot
6 · Hermes darpa
7 · 2 leg robot
$10K+
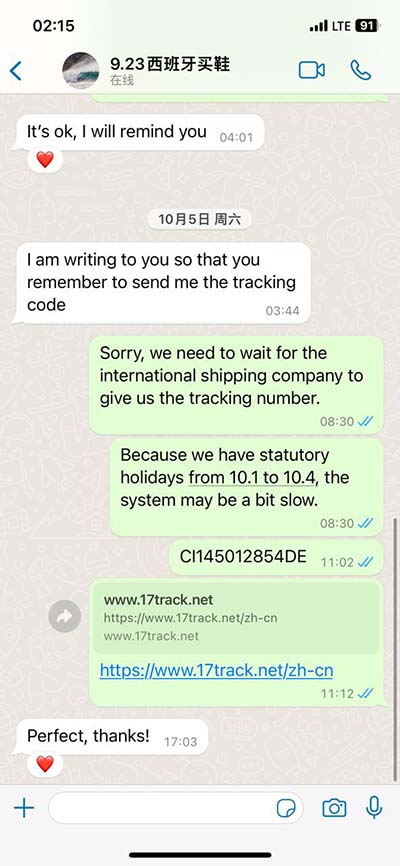
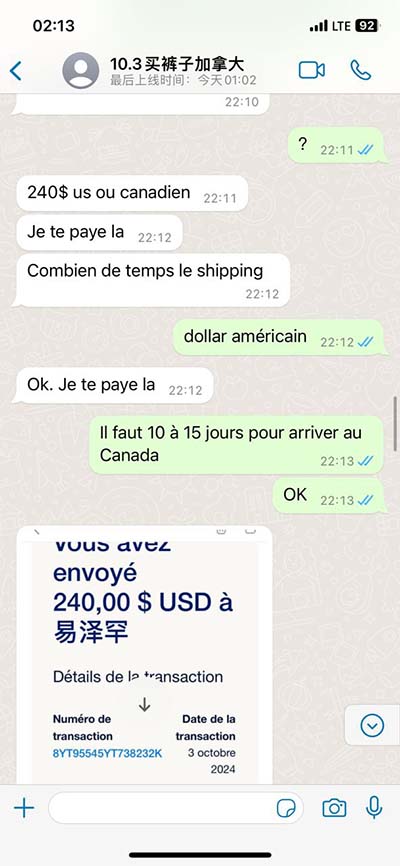
Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash . Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response. Ramos’s reflexes .Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, . Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.
Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response. Ramos’s reflexes help HERMES keep its footing.Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half. Engineers have developed a way to control balance in Little HERMES, a two-legged, teleoperated robot — an essential step toward enabling a humanoid to carry out high-impact tasks in challenging environments. The work was done at MIT and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
HERMES is a disaster response robot from MIT based on the Cheetah Robot, developed by Professor Sangbae Kim and his group at the MIT Biomimetic Robotics Lab. To experimentally demonstrate this strategy, we developed a wearable HMI, named the balance feedback interface (BFI), and a small-scale bipedal robot, named Little HERMES . This work focused on studying fundamental locomotive skills such as synchronous stepping, jumping, and walking via teleoperation. He now has a new partner in those endeavors: Hermes, a humanoid robot manufactured by Sarcos U.S., one of the world’s premier robotics companies. Hermes is one of only four robots of his type ever made; two are in use in Japan, and one is .Little HERMES is a small-scale bipedal robot designed for studying balancing strategies. Due to its small size, it is inherently safer to perform experiments than the full-scale robot HERMES. Each leg is torque controlled, highly backdrivable and has 3 DoF.
A two-legged robot named HERMES, outfitted with load sensors, can punch through drywall, smash soda cans, and karate-chop boards in half, but its actions are not its own. A few feet away, MIT Ph.D. student Joao Ramos stands on a platform, wearing an . Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half. Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response. Ramos’s reflexes help HERMES keep its footing.
Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.
little Hermes robot
Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half. Engineers have developed a way to control balance in Little HERMES, a two-legged, teleoperated robot — an essential step toward enabling a humanoid to carry out high-impact tasks in challenging environments. The work was done at MIT and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. HERMES is a disaster response robot from MIT based on the Cheetah Robot, developed by Professor Sangbae Kim and his group at the MIT Biomimetic Robotics Lab.
To experimentally demonstrate this strategy, we developed a wearable HMI, named the balance feedback interface (BFI), and a small-scale bipedal robot, named Little HERMES . This work focused on studying fundamental locomotive skills such as synchronous stepping, jumping, and walking via teleoperation. He now has a new partner in those endeavors: Hermes, a humanoid robot manufactured by Sarcos U.S., one of the world’s premier robotics companies. Hermes is one of only four robots of his type ever made; two are in use in Japan, and one is .Little HERMES is a small-scale bipedal robot designed for studying balancing strategies. Due to its small size, it is inherently safer to perform experiments than the full-scale robot HERMES. Each leg is torque controlled, highly backdrivable and has 3 DoF.
humanoid biped robot

bipedal humanoid
biped robots
5 Reasons to Buy a Rolex Explorer II. Additional 24-hour display; Second time zone display; COSC-certified in-house calibers; Water-resistant to 100 m (10 bar, 328 ft), stainless steel Oyster case; Excellent financial performance
hermes robot|bi pedal robot